Intraventricular Hemorrhage
The germinal matrix is a region in the developing fetus that is located next to the ventricles (periventricular) and gives rise to neurons and glial cells. It is highly vascularized with fragile capillaries that can easily rupture. This region involutes by 32 weeks of gestation. There is supporting structures around it that develop and protect it. In premature babies born before 32 weeks, the germinal matrix has not involuted putting them at risk for rupture of the fragile capillaries leading to intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH). In very low birth weight newborns, <1500g, the risk of germinal matrix capillary rupture is also increased.

The blood coagulates and can be easily visualized with a cranial ultrasound in the preterm newborns — ultrasound has no radiation and is sensitive for coagulated blood. The blood has increased echogenicity compared to the nearby CSF and brain parenchyma.
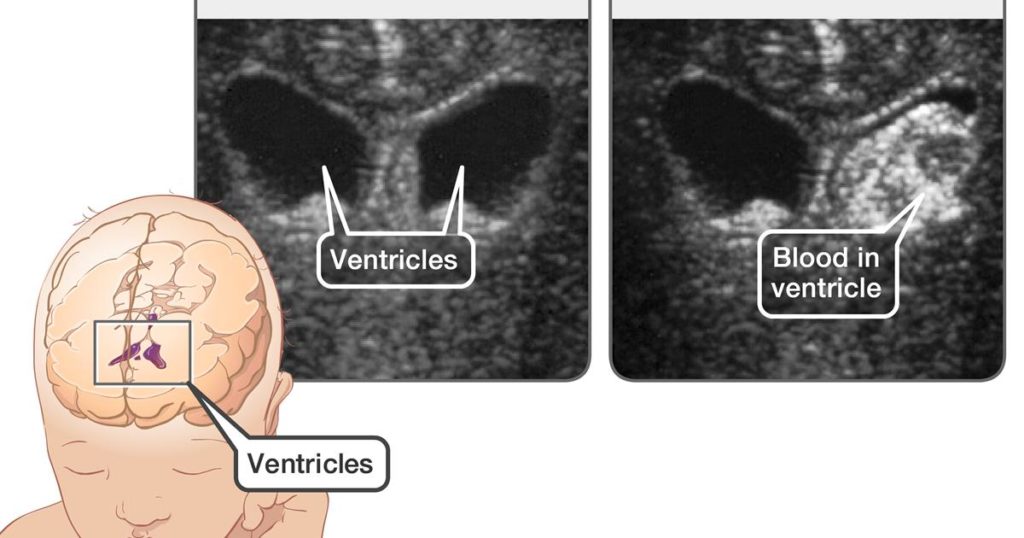
Because of the increased risk in preterm infants born <32 weeks, all babies born <32 weeks require a cranial ultrasound at ~1-2 days of age. About 50% of IVH cases are asymptomatic and found on screening cranial ultrasound.
Newborns who present with symptoms may present as:
- 3-4 day old preterm newborn (<32 weeks gestation) with anemia, seizures, hypotonia and decreased movements, lethargy, apnea, bulging fontanelle, rapidly increasing head circumference, tachycardia or bradycardia (Cushing reflex)
Management includes
- Stabilize Blood pressure
- anti-seizure medications
- Monitor for complications using repeat cranial ultrasounds — looking for posthemorrhagic ventricular dilation
