Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES)
A 32 year old comes to your clinic complaining of difficulty swallowing with solids, as well as both hot and cold liquids. This has been happening intermittently for about a week.
Pathology
Impaired innervation of the esophagus –> uncoordinated simultaneous contractions (non-peristaltic). This primarily affects the distal esophagus, so this condition is also called Distal Esophageal Spasm (DES).
Presentation
Spontaneous odynophagia and dysphagia with both solids and liquids. May be described as “chest pain” when eating. Often precipitated by emotional stress. The chest pain is relieved by nitroglycerin and calcium channel blockers — they relax the esophageal myocytes. They often have regurgitation of food.
Key features:
- – progressive dysphagia to solids & liquids
- – chest pain or odynophagia
- – regurgitation of food
Diagnosis
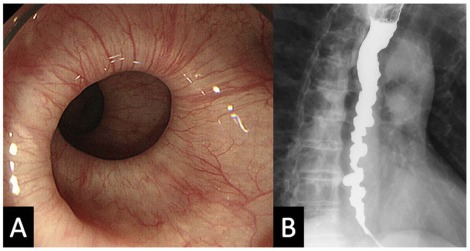
Barium swallow (esophogram) will show a “corkscrew” pattern and dilation of the proximal esophagus.
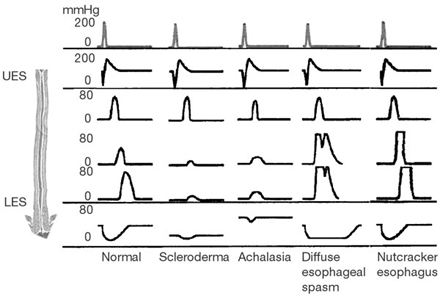
Manometry will show intermittent peristalsis with many contractions that are not peristaltic.
Key features:
- – Upper GI endoscopy: circular folds in esophagus i.e. “corckscrew” pattern
- – Barium swallow: constricted, twisted esophageal lumen i.e. “corckscrew”
Treatment
Calcium channel blockers e.g. diltiazem. Can also use nitrates and tricyclics. May need ballon dilatation. Because patients often have GERD in addition to DES, a trial of PPIs might be helpful.
