Esophagus in Scleroderma
IM→GI→Esophagus→Motility Disorders→Scleroderma
A 35 year old African American woman presents to your clinic with difficulty swallowing and heart burn. History reveals a diagnosis of scleroderma.
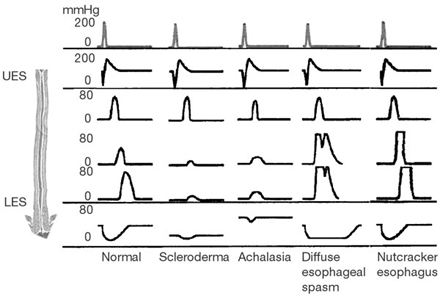
Pathology: Scleroderma causes diffuse fibrosis of the esophagus which results in loss of LES (lower esophageal sphincter) function as well as absent peristalsis of smooth muscle in the distal esophagus.
Presentation: Patients present with dysphagia as well as GERD. They will have history of scleroderma, look for a description of Raynaud’s phenomenon.
Diagnosis: Manometry will show hypotensive/ absent peristalsis and LES tone.
Management: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).