-
Acute Kidney Injury
Topics: Categorizing acute kidney injury, Approach to acute kidney injury, Acute kidney injury requiring dialysis. Categorizing Acute Kidney Injury Acute kidney injury can be categorized into 3 main groups: pre-renal, renal and post-renal. Any problems with the heart, or blood supply reaching the kidneys is considered pre-renal. Any problems inside the kidney itself is considered intra-renal. Any problems occurring with urine being able to leave the kidneys i.e. in the ureters, bladder, urethra is post-renal. Post-renal AKI is kidney damage due to back up of urine produced by the kidneys into the kidney itself. Pre-renal AKI is kidney damage due to a lack of blood flow to the kidneys. Intra-renal…
-
Renal Cysts and Renal Cancer
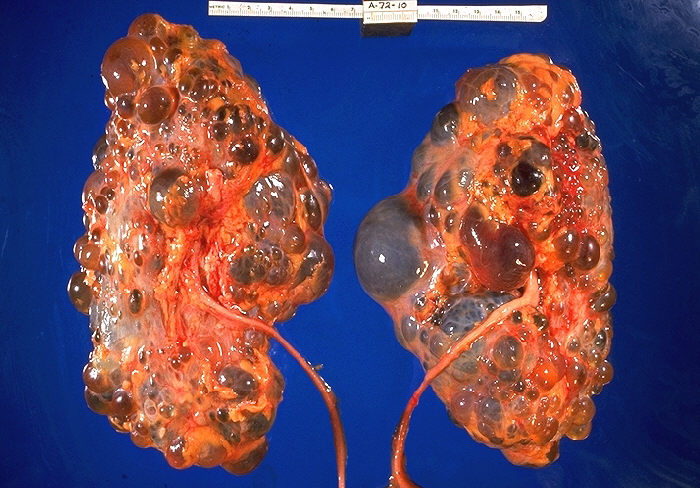
Topics: Simple Cysts, Complex Cysts, Renal Cell Carcinoma, Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPCKD), Autosomal Dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPCKD). Simple Cysts Presentation: Small cyst found on asymptomatic screen i.e. incidental cyst. No loculations or septations. Diagnosis: no further testing required Treatment: no treatment required Complex Cysts Presentation: Can also be found on asymtomatic screen, and will have septations and loculations. However, may present similar to a kidney stone (flank pain and hematuria) or similar to renal cell carcinoma (flank mass, flank pain, hematuria), or with pyelonephritis (when cyst becomes infected). Diagnosis: Because of the way it presents, a urinalysis and CT scan will usually be done. If pregnant or…
-
Liver Tests
What is the most specific liver test? AST, ALT, ALP, or albumin Aminotransferases AST and ALT are liver enzymes that catalyze transfer of amino groups in gluconeogenesis. AST catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from aspartic acid to ketoglutaric acid to produce oxaloacetic acid. ALT catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from alanine to ketoglutaric acid to produce pyruvic acid. AST is found in many tissues including the liver, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, kidney, brain, pancreas, lungs and red blood cells. ALT is found mainly in the liver and is more specific for liver disease than AST. Alkaline phosphatase ALP is found in the liver, but also in…
-
Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score
The CTP score is used to predict surgical risks in patients with cirrhosis when undergoing intra-abdominal operations. Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) Score Variable 1 point 2 points 3 points Bilirubin < 2 mg/dL 2-3 mg/dL > 3 mg/dL Albumin >3.5 g/dL 2.8-3.5 g/dL
-
Acalculous Cholecystitis
What causes acalculous cholecystitis? The gallbladder in acalculous cholecystitis has stasis of bile within it and is also hypoperfused leading to inflammation (cholecystitis). By definition it is cholecystitis that occurs without a gallstone being present in the gallbladder. What are some risk factors for developing acalculous cholecystitis? Acalculous cholecystitis is typically seen in patients that are critically ill. Risk factors include: immunosuppression recent surgery total parenteral nutrition (TPN) sepsis hypotension How is the diagnosis of acalculous cholecystitis made? The diagnosis is made based on findings in the history and physical exam along with laboratory tests and imaging. Suspect acalculous cholecystitis in patients with risk factors (recent surgery, TPN, etc) who have…
-
Acetaminophen
A 35 year old man is brought to the ED by a friend after he attempted to commit suicide by ingesting a bottle of acetaminophen. What is the next best step in management? Presentation Day 1 (first 24h) nausea vomiting Day 2-3 (48-72h) hepatic failure Amount ingested 10 g is toxic 15 g is fatal amounts are lower if liver disease or alcohol abuse Diagnosis Acetaminophen level: get this if the amount ingested is not known and not sure if it was enough to cause toxicity. Remember, treatment is more important than knowing the acetaminophen level, so give N-acetylcysteine right away if suspected overdose, don’t wait on the acetaminophen level.…
-
Manometry
Esophageal manometry is an accurate method for assessing esophageal motility disorders including achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm and scleroderma affecting the esophagus.
-
Dysphagia Qs
Loading…
-
Esophagus in Scleroderma
IM→GI→Esophagus→Motility Disorders→Scleroderma A 35 year old African American woman presents to your clinic with difficulty swallowing and heart burn. History reveals a diagnosis of scleroderma. Pathology: Scleroderma causes diffuse fibrosis of the esophagus which results in loss of LES (lower esophageal sphincter) function as well as absent peristalsis of smooth muscle in the distal esophagus. Presentation: Patients present with dysphagia as well as GERD. They will have history of scleroderma, look for a description of Raynaud’s phenomenon. Diagnosis: Manometry will show hypotensive/ absent peristalsis and LES tone. Management: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
-
Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES)
A 32 year old comes to your clinic complaining of difficulty swallowing with solids, as well as both hot and cold liquids. This has been happening intermittently for about a week. Pathology Impaired innervation of the esophagus –> uncoordinated simultaneous contractions (non-peristaltic). This primarily affects the distal esophagus, so this condition is also called Distal Esophageal Spasm (DES). Presentation Spontaneous odynophagia and dysphagia with both solids and liquids. May be described as “chest pain” when eating. Often precipitated by emotional stress. The chest pain is relieved by nitroglycerin and calcium channel blockers — they relax the esophageal myocytes. They often have regurgitation of food. Key features: – progressive dysphagia to…