-
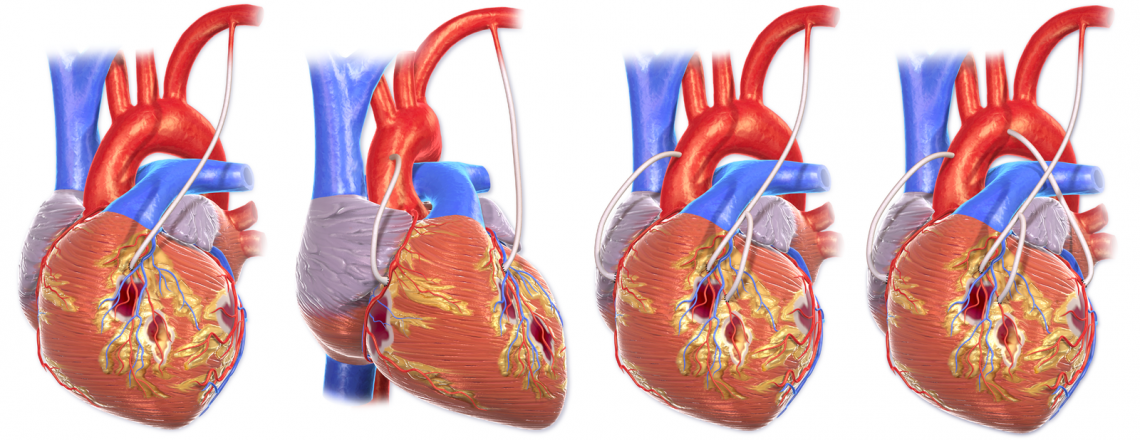
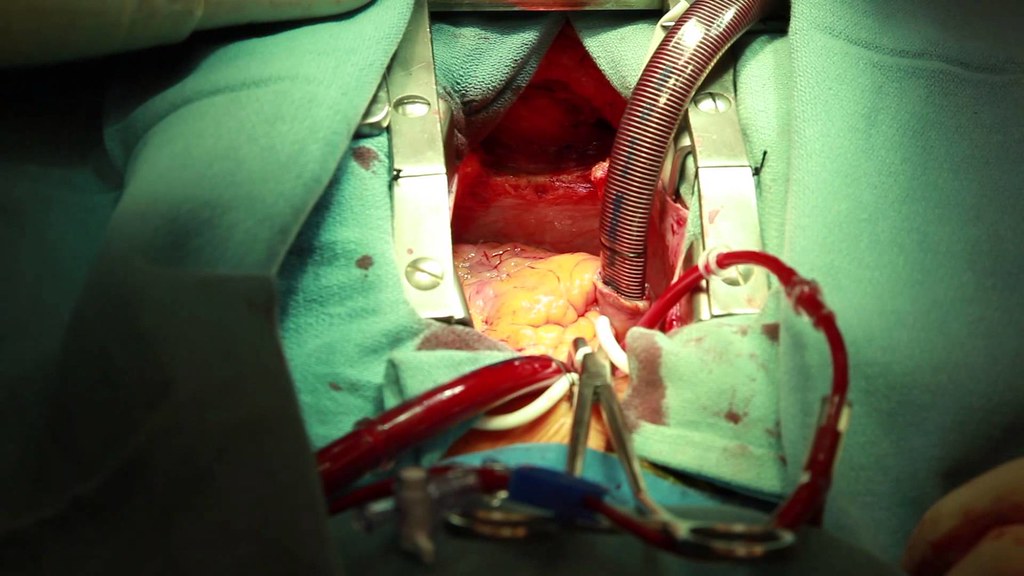
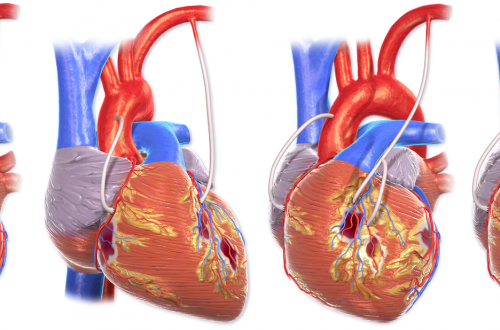
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
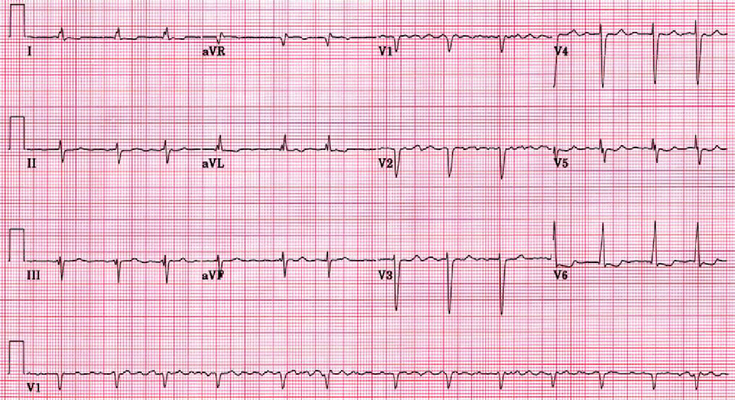
The goal of CABG is to restore blood flow to the myocardium. Preoperative Care During preoperative assessment of patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting, special care should be paid to the severity of their coronary artery disease, their vascular function, the presence of comorbid disease, and explaining to the patient the procedure and postoperative care expectations. Medications Cardiac medications are to be continued up to the morning of the operation, except ACE inhibitors and digoxin. Monitoring Routine monitoring of CABG patients often includes: 5 lead ECG Temperature – core temperature (nasopharyngeal) Pulse oxymetry Capnography Central venous pressure Invasive BP monitoring Anesthesia for CABG An example protocol for induction: Etomidate, Fentanyl,…
-
Croup
Patient Care Precautions and Safety: Isolation: Contact and Droplet Activity: Activity as Tolerated Diet For child who has been recently moderately or severely distressed: Clear Fluids During periods of moderate to severe respiratory distress: NPO For mild croup: Regular Diet Respiratory Care Supplemental oxygen need should prompt urgent physician assessment and concern for possible progressive upper airway obstruction. O2 Therapy – Titrate to maintain saturation above 92%. Place the patient on supplemental oxygen to maintain oxygen saturation level greater than 92% AND notify physician of NEW oxygen requirement immediately. Monitoring For mild symptoms consider vital sign monitoring every 4 hours and more frequent for moderate or severe symptoms. Vital signs…
-
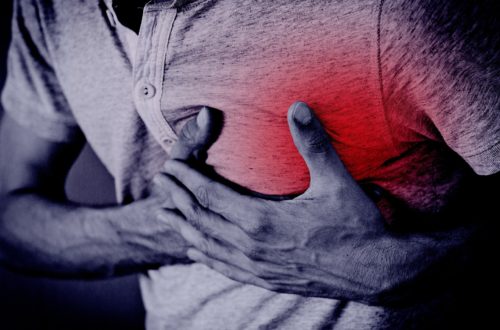
Chest Pain
Intravenous Fluid Orders Intravenous Cannula – Insert IV Peripheral Saline Flush/Lock: Saline Lock IV Maintenance: 0.9% NaCl infusion at ______ mL/hour, reassess after hours lactated ringers infusion at ______ mL/hour, reassess after hours IV Bolus: 0.9% NaCl ______ mL over ______ hour(s) lactated ringers _______ mL over _______ hour(s) Laboratory Investigations Hematology Complete Blood Count (CBC) PT INR Chemistry Troponin Repeat Troponin_________time(s) (specify collection time below) ___________:_____________ ___________:_____________ Electrolytes (Na, K, Cl, CO2) Glucose Creatinine Urea Serum bHCG Urine Tests Urine Dipstick Testing – POCT Urinalysis Pregnancy Test, Urine (POCT if available) Other Labs (based on presentation needs of the patient) Diagnostic Imaging Chest x-ray usually indicated unless recently performed to rule out…
-
Acute Coronary Syndromes
Checklist ECG: Get a 12 lead ECG within 10 minutes of patient presenting with chest pain Vitals: Take initial vital signs: temp, HR, RR, SpO2, BP in both arms; and repeat if there further chest pain or equivalent symptoms Oxygen: Give Oxygen if SpO2 ≤ 90% or there are clinical signs of hypoxemia Antiplatelets: Give acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin®) now if it was not given prior to arrival at hospital. Write down when it was given. Nitroglycerin: Give Nitroglycerin in hemodynamically stable patients every 5 minutes as needed. *Avoid if suspected RV infarction. Dose: usually 0.3 to 0.4 mg. Place defibrillation pads on chest – because there is a high risk…
-
Bias in Research Studies
Bias refers to a systematic error in a research or statistical study. The first large category of bias we will look at is selection bias. Selection bias occurs when those selected for a study are not properly selected or when they are not all retained in a cohort study. The following are subtypes of this bias. Sampling bias also called ascertainment bias occurs when the study population is different from the target population because during selection of subjects there was no randomization. Remember, we can not put the entire population into a study, so the sample we select should be as representative as possible. To do this, we can use…
-
Endocrinology – topics
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Neuroendocrinology Pituitary masses and tumors Posterior pituitary disorders Thyroid Diagnostic testing for suspected thyroid disease Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism & Thyroiditis Nontoxic diffuse goiter Thyroid nodule Thyroid cancer Adrenal Cortex Adrenal cortex Endocrine hypertension Endocrine pancreas Type 2 diabetes mellitus Type 1 diabetes mellitus Hypoglycemia Obesity Lipid disorders Mineral Metabolism Osteoporosis Rickets & Osteomalacia Kidney stones Reproductive endocrinology Hormonal contraception Hormonal therapies Testicular disorders Pregnancy and endocrine changes Pediatric endocrinology Disorders of sexual development Growth disorders Multi-organ endocrine disorders Multiple endocrine metaplasia (MEN) HIV/AIDs – endocrine problems
-
Sarcoidosis
multisystem disease characterized by non-caseating granulomas etiology is unknown Presentation Lungs: dry, non-productive cough, dyspnea, chest pain Eyes: blurry vision, conjunctivitis, eye pain, uveitis (common), iritis Skin: erythema nodosum, papules, macules, nodules, lupus pernio Heart: arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy Diagnosis diagnosis of exclusion initial labs: CBC, serum chemistry (ALT, AST, ALP, BUN, Cr, Ca, other electrolytes), urinalysis, 24 h urine excretion of calcium, CRP, ESR, tuberculin skin test imaging: CXR, ECG pulmonary function tests: spirometry, diffusion capacity of carbon monoxide (DLCO)- single breath biopsy (skin, lymph nodes or conjunctiva) of affected area, and if no suitable area is present then bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsy. Management Corticosteroids are the mainstay therapy when required.…
-
Hypercalcemia
Normal Ca in mg/dL: 8.4 – 10.2 (lab value from nbme.org) Normal Ca in mmol/L: 2.18 – 2.58 (lab value from mcc.ca) Sample Case: A 40 year old man arrives in the clinic complaining of polyuria, constipation and malaise. He has normal vital signs and no significant findings on physical exam. On laboratory testing, his serum calcium is elevated at 11 mg/dL (2.74 mmol/L). What is the best next step in management? First, you need to recognize that he has hypercalcemia. The most common cause of hypercalcemia in patients arriving in the clinic is primary hyperparathyroidism. To diagnose hyperparathyroidism, you first need to get the parathyroid hormone (PTH) level. Remember,…
-
How to Study for Step 1 Usmle
Step 1 is probably going to be one of the most difficult exams you will write in your medical career. Scoring well on this exam is necessary for matching into your residency of choice. So, the question is, what is the best approach to ace your exam? We’ve looked at advice and comments from past test takers to come up with the best test resources, schedules, and study approaches. First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 To ensure that you cover all the most important topics, you will need a a general review book. First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 is the best book for this. It lacks detailed…
-
Hot Tub Folliculitis
This an infection of the hair follicles caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. There is often a history of emersion in hot tubs, whirlpools or other sources of contaminated water. The rash that occurs is often worse if the skin is occluded by a bathing suit. The rash can present anywhere from a few hours to days after exposure, and consists of itchy red bumps and may progress to tender nodules filled with pus. Hot tub folliculitis is self-resolving within 5 to 10 days but may leave a reddish-brown or hyperpigmented area that can take a few months to disappear. To help with the rash, white vinegar can be applied for 20…